Authentication Methods - A Deep(ish) Dive
Feb. 27, 2025Here lies the ramblings of a madwoman; bumbling her way around in the darkness in an attempt to understand the wide world of websec…
… in the absolute broadest of strokes:
- Token-based (
JWT):- Authentication state is stored on the client (local/session storage) in the form of a token.
- Session-based:
- Authentication state is stored on the server’s database.
Now, let’s go a little deeper, shall we?
- JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
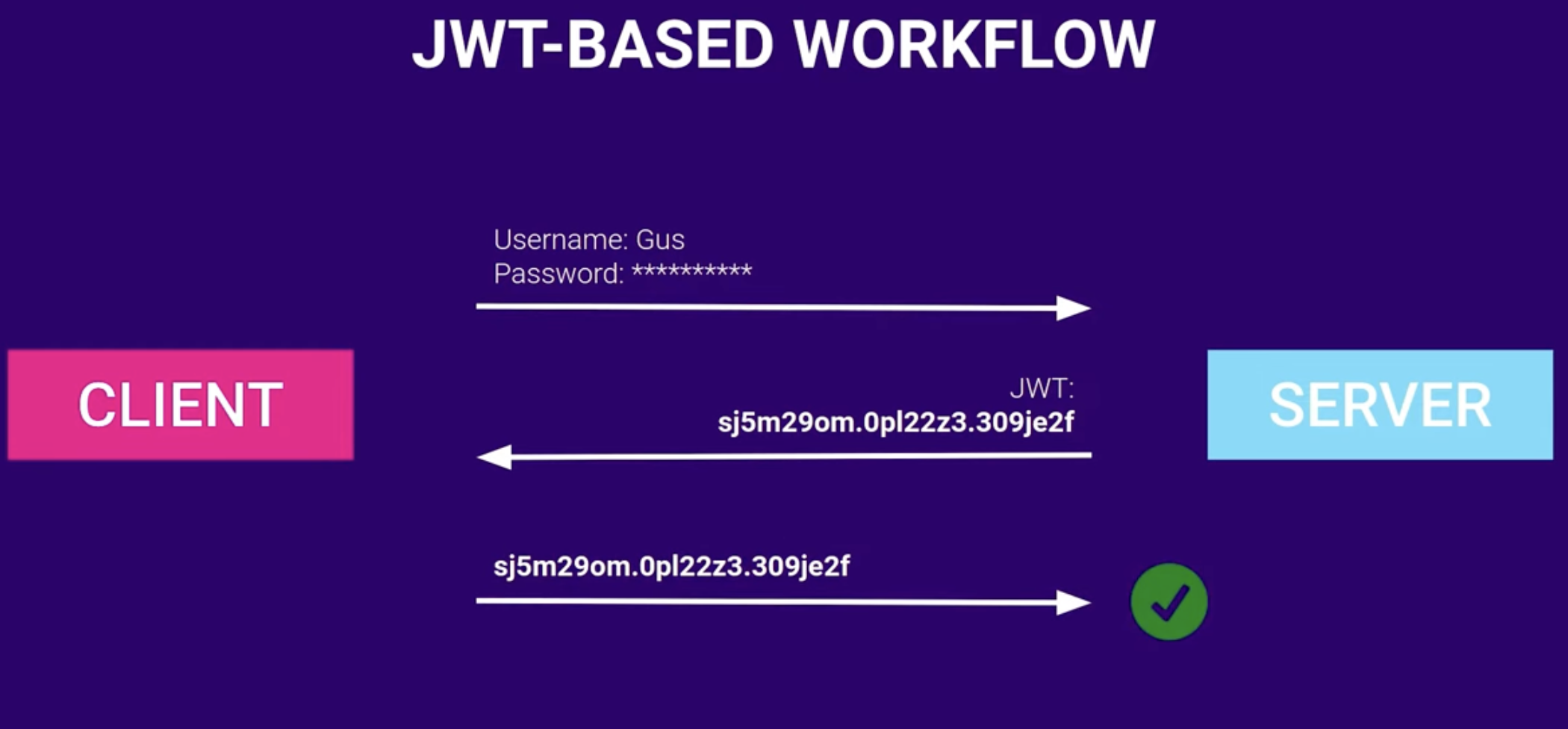
- How it works:
- Client sends credentials to sever
- Sever generates a
JWTbased on credentials, and provides it to user (following below structure).- For example, using the
RS256algorithm, the generatedJWTis signed with the server’s private key, and verified by the client with the server’s public key.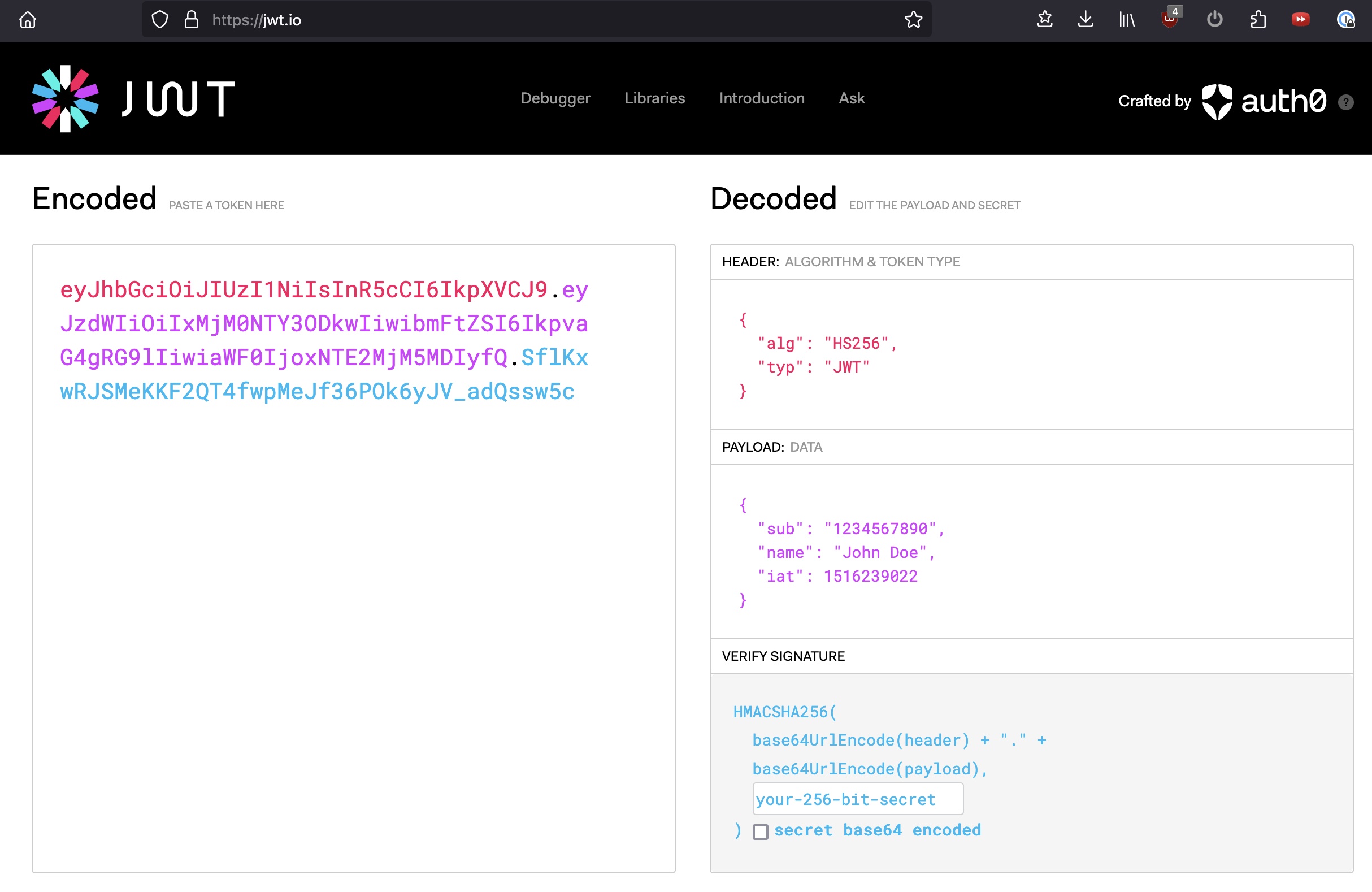 (
(JWTstructure - https://jwt.io/)
- For example, using the
- The client receives the
JWT, which is stored in the client’s local storage/session storage/as a cookie. AKA, the state lives as a token on the client, instead of on the server (as is with typical session-based authentication).- Note: the client also verifies the
JWTwith the server’s public key, if using theRS256algorithm.
- Note: the client also verifies the
- JWT-based Authentication Drawbacks
- State is stored client side & can thus be dissected & manipulated
- Vulnerable to being accessed/stolen via XSS attacks
- Can be vulnerable to CSRF based on how the
JWTis stored & sent.- Vulnerable to CSRF: if the
JWTis stored as anHTTP-only cookie that is passed to the server with every request.- to mitigate this, use
SameSite=Strict& additionalCSRFtokens with each request.
- to mitigate this, use
- NOT (as) vulnerable to CSRF: if the
JWTis stored in thelocal/session storage, meaning it’s not sent with every request. Instead, it must be manually passed into the request header (e.g.Authorization: Bearer <token>) when authorising.
- Vulnerable to CSRF: if the
- No server-side revocation - token is valid until it expires.
- Token expiration management can be complex
- Data is
base64encoded, not encrypted - so sensitive data should never be stored in JWTs, as anyone with the token can decode and read its contents.
- Session-based (cookie) authentication:
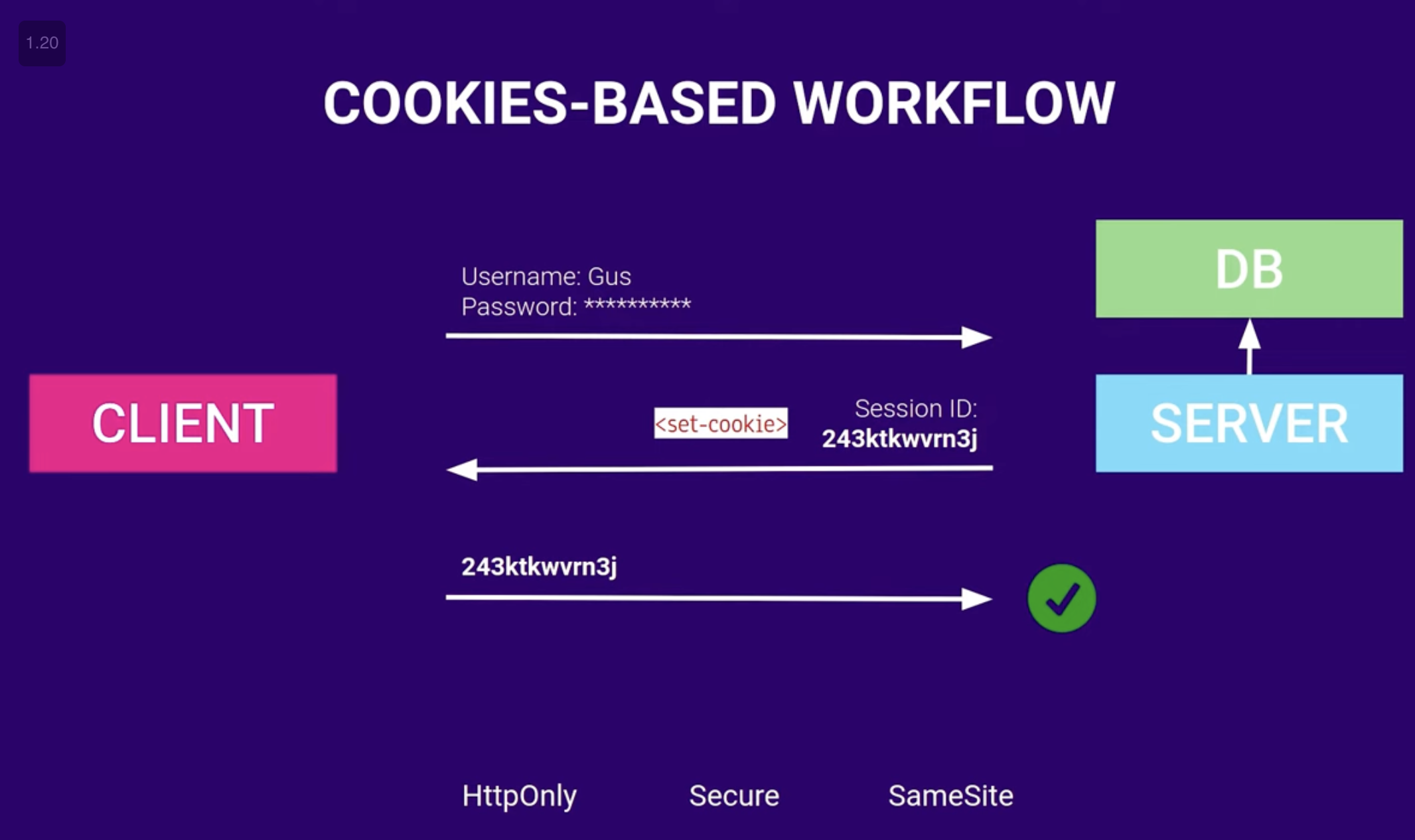
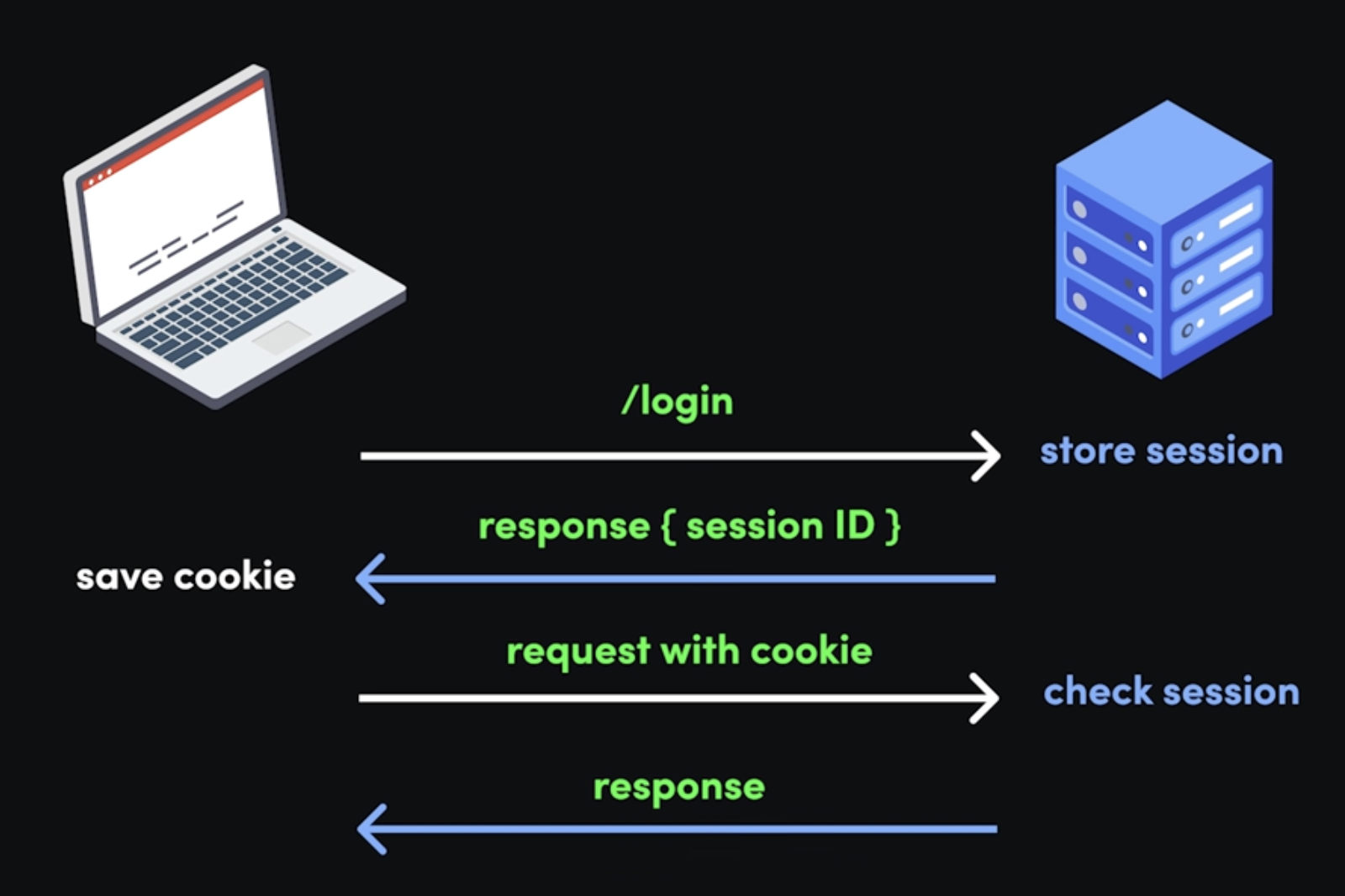
- How it works:
- Client provides credentials to the server
- Server generates a unique session ID for the client and stores the session details & state in its local database.
- Server sends the session ID back within an
HTTP-onlycookie, which is stored in the client browser’s cookie jar (a storage for key-value pairs - how cool is this name though-) - The client sends this cookie back with subsequent requests, & each time, the server has to check the session against the value in the server’s database.
- Upon logout, session ID is cleared from both the client side and server database.
- Session-based Authentication Drawbacks:*
- Vulnerable to CSRF (attackers using session IDs to perform actions on behalf of the user) as cookies are sent automatically with every request.
- Processing power & complexity that increases with scale: as sessions have to be generated, stored & managed on the server’s database.
- Domain Restriction: Cookies are domain-specific, making cross-domain authentication difficult without additional configurations like
CORS(Cross Origin Resource Sharing) or third-party cookies.CORS: when a web app makes a cross-origin request (e.g.example.comtoapi.example.com), the browser sends an additionalCORSpreflight request to check if the server (api.example.com) allows the cross-origin request. If it does, it needs to respond with the appropriateCORSheaders.
A brief comparison…
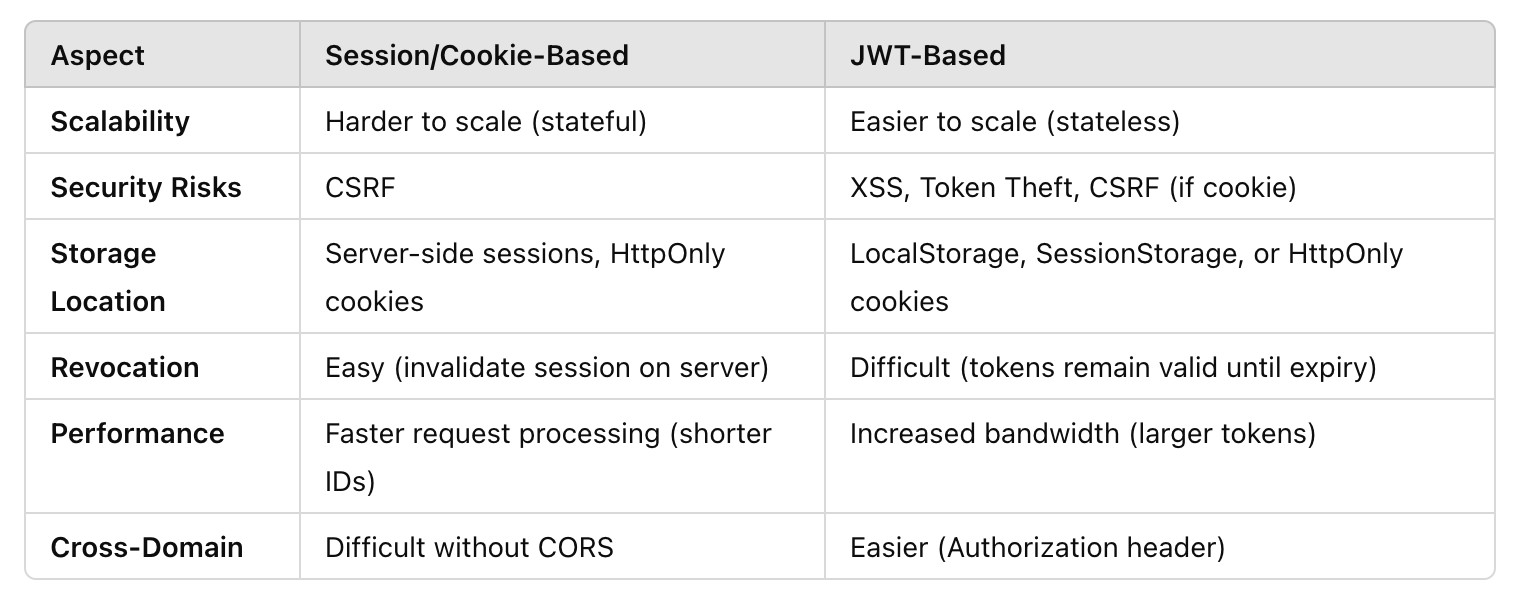
credit where credit is due, this is from ChatGPT, but it was used as a sanity check after I did the bulk of the manual research to build a basis of understanding. so, what am i saying by this? take… all of it with a grain of salt lol-
Helpful Resources: